-
Your shopping cart is empty!

This article as been cited by other articles from references below.
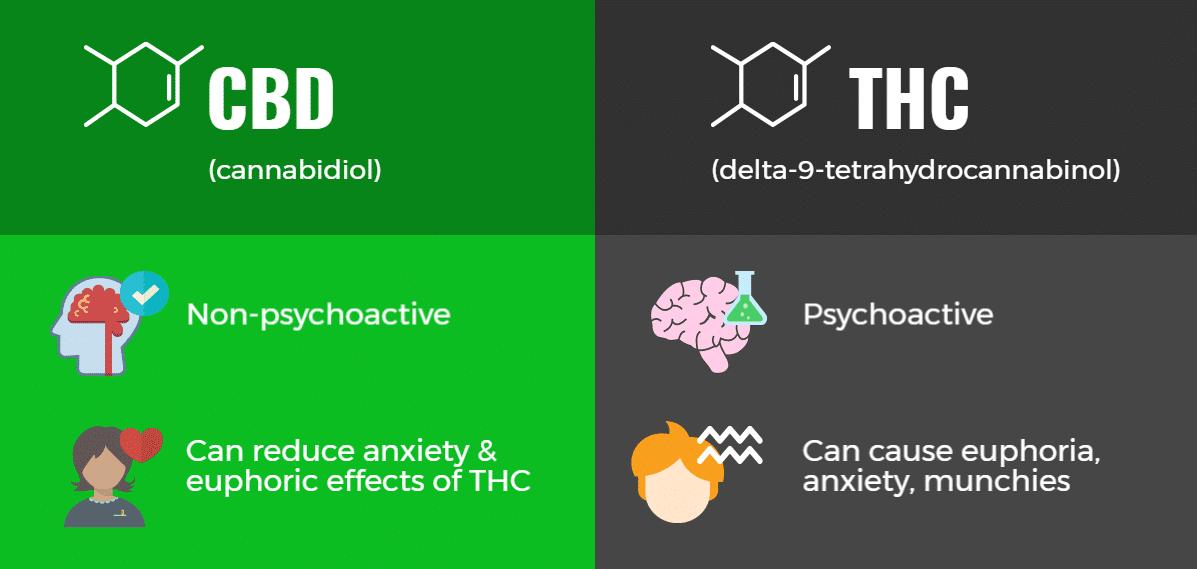
CBC & THC
Cannabis is a complex plant, with major compounds such as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol, which have opposing effects. The discovery of its compounds has led to the further discovery of an important neurotransmitter system called the endocannabinoid system. This system is widely distributed in the brain and in the body, and is considered to be responsible for numerous significant functions. There has been a recent and consistent worldwide increase in cannabis potency, with increasing associated health concerns. A number of epidemiological research projects have shown links between dose-related cannabis use and an increased risk of development of an enduring psychotic illness (Zerrin Atakan, 2012).
CBD is a close relative to THC, and these two substances make up only two of over 85 various cannabinoids within the marijuana plant. THC has a different effect than CBD on your body because CBD is not psychoactive. So, you will not experience altered perceptions from CBD, as you would from THC. Every marijuana plant contains unique amounts of both THC and CBD. All plants vary in this regard. It all depends on the purpose, and how they are grown. For example, if someone grows marijuana for recreational purposes, it will tend to have more THC and CBD. You will find that manufactured hemp plants have very small amounts of THC. Lastly, medical marijuana will usually have a much higher rate of CBD (Bergman, 2016).
Cannabis products are used for medicinal and industrial purposes, as well as for intoxication. At least four US states and one EU Member State now have two separate distribution systems for intoxicating cannabis running in parallel, besides any industrial use of the non-psychoactive parts of the plant. Clarity is needed when discussing the laws involved. Cannabis products that are used for medicinal purposes — whether the psychoactive THC or the non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) — are generally referred to as ‘medical cannabis’. Cannabis products used in manufacturing are commonly referred to as ‘industrial hemp’. Cannabis products used for non- medical intoxication have been variously referred to as non-medical cannabis, retail cannabis and recreational cannabis (European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction, 2018)
CBD
Cannabidiol, or CBD for short, tends to be the second most abundant cannabinoid in marijuana. It has serious implications into the field of medicine, and is the sought after compound by medical users. It is a non-psychoactive component that is believed to reduce and regulate the effects of THC. This means that strains high in THC and CBD will induce much clearer head highs than more hazy, heady strains containing very little CBD (Zamnesia, 2018).
CBD itself has a long list of medicinal properties. The main of which relieve things such as chronic pain, inflammation, migraines, arthritis, spasms, epilepsy and schizophrenia. CBD has also been show to have some anti cancer properties, and new uses are being found all the time as more research is conducted (Zamnesia, 2018).
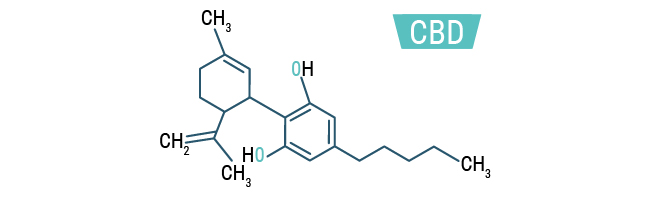
Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the naturally occurring cannabinoids found in cannabis plants. It is a 21-carbon terpenophenolic compound which is formed following decarboxylation from a cannabidiolic acid precursor, although it can also be produced synthetically. In experimental models of abuse liability, CBD appears to have little effect on conditioned place preference or intracranial self-stimulation. In an animal drug discrimination model CBD failed to substitute for THC. In humans, CBD exhibits no effects indicative of any abuse or dependence potential. CBD has been demonstrated as an effective treatment of epilepsy in several clinical trials, with one pure CBD product (Epidiolex®) currently in Phase III trials. There is also preliminary evidence that CBD may be a useful treatment for a number of other medical conditions. There is unsanctioned medical use of CBD based products with oils, supplements, gums, and high concentration extracts available online for the treatment of many ailments. CBD is generally well tolerated with a good safety profile. Reported adverse effects may be as a result of drug-drug interactions between CBD and patients’ existing medications. Several countries have modified their national controls to accommodate CBD as a medicinal product. To date, there is no evidence of recreational use of CBD or any public health related problems associated with the use of pure CBD (WHO,2017).
CBD has many potential benefits, some mirroring the benefits of THC. These include reducing nausea and PTSD, as well as treating migraines and inflammation. For those seeking the medical benefits of marijuana, without any risk of being high, CBD oil provides a practical solution (Bergman, 2016).
Beware cheap imitations
With the popularity and effectiveness of CBD, it’s probably no surprise that there are imitators. Just like there is fake weed, there are also synthetic cannabinoids. These man-made CBD alternatives are added to dried plant materials to give the appearance of CBD-rich marijuana or sold as liquids for e-cigarettes. Many times, the products are labeled as ‘synthetic marijuana’ or ‘legal weed.’ While CBD oil is not marijuana or weed, it too can be imitated with synthetic cannabinoids. The problem with these chemicals is that they are not researched, and may not be safe. In some cases, people have had severe reactions to synthetic cannabinoids. Sometimes avoiding these dangerous products is as easy as reading the fine print. Some products clearly state they are ‘not for human consumption.' Another way to avoid buying imitation CBD is by purchasing from a reliable source (Bergman, 2016).
THC
THC has the ability to change a person’s behavior by connecting to the receptors on the nerve cells, which in turn results in a change of activity. In certain parts of the brain that are connected with memory, coordination, thinking, pleasure and time perception, the cannabinoid receptors are concentrated. Nerves in other parts of our bodies also have cannabinoid receptors. The THC will alleviate pain, but it won’t bind itself to the receptors in the brain in the same way that opioids like morphine, heroine and other drugs that come from the poppy plant do. THC creates euphoria by stimulating the cells in the brain which releases dopamine. THC also interferes with the way the brain processes and forms new memories (Royal Queen Seeds, 2014).
It can cause a person to have hallucinations and delusions we well as change the way they think. All of these effects of marijuana make the drug a popular one, but in some instances, this concerns mental health advocates. The National Institute on Drug Abuse indicates that using THC can trigger some schizophrenic symptoms. The compound THC is also known to give a person the “munchies” due to stimulation of the appetite. It also induces a person to be in a relaxed state and has an effect on a person’s sense of smell, eyesight and hearing. It is known to cause fatigue, and in some people, it does lessen the symptoms of aggression. Some studies have shown THC works well for treating vomiting and nausea, and it has some anti-emetic qualities (Royal Queen Seeds, 2014)
This is the most commonly recognized and abundantly found cannabinoid within cannabis; it stands for delta-9-tetrahydrocannibinol. This cannabinoid is responsible to the main psychoactive effect experienced when consuming cannabis, it stimulates parts of the brain causing the release of dopamine – creating a sense of euphoria and well being. THC also has analgesic effects, relieving the symptoms of pain and inflammation. Combined they cause a great sense of relaxation (Zamnesia, 2018).
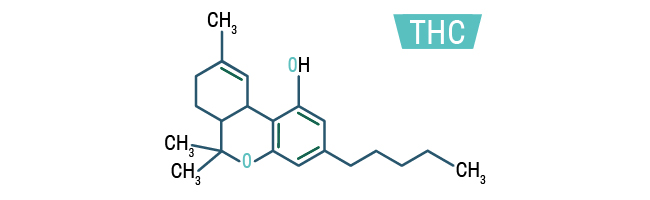
THC chemical structure (Zamnesia, 2018)
THC is a psychoactive compound (meaning it affects brain function by acting on the central nervous system, which can result in altering your mood, behavior, perception and cognition) and its effects are what users of cannabis feel the most when smoked. The high is responsible for the feeling of relaxation, the heightening of your. It also has medicinal uses for a multitude of symptoms including; mild to moderate pain, insomnia, depression, nausea and appetite loss, just to name a few. For some people though THC may cause anxiety or paranoia, often related to the feeling of time slowing down, which it of course is not (Royal Queen Seeds, 2014).
While both the THC and CBD cannabinoids individually have many beneficial properties when they are used together, as they come from the marijuana plant, their effects are far more impressive. When working alongside of the THC molecules CBD can negate some of the anxiety that THC causes as well as give relief for different types of pain than THC can. This makes nature the best doctor by combining them into a single plant because they are way more effective when administered together, especially for people with multiple symptoms (Royal Queen Seeds, 2014).
One unique difference between THC and CBD is that CBD does not bind to the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors on your cells like THC does. Another way of saying it is the CBD molecule does not align, and therefore, it has a different effect on your body's cells (Bergman, 2016).
HappHEMP products are produced exclusively from natural ingredients using supercritical CO2 extracti..
43.00€ Ex Tax: 43.00€
HappHEMP products are produced exclusively from natural ingredients using supercritical CO2 extracti..
0.00€ Ex Tax: 0.00€
HappHEMP products are produced exclusively from natural ingredients using supercritical CO2 extracti..
73.00€ Ex Tax: 73.00€